All vehicle owners in India need to pay road tax, a compulsory payment to state governments to facilitate the upkeep and creation of the public roads, highways, and other transport infrastructure. In Haryana, revenue collected from road tax plays a central role in maintaining the road network and providing a smooth and safe journey to everyone.
The knowledge of calculating road tax, the different tax rates and the existing payment options is especially essential among vehicle owners in Haryana so that they do not fall short of paying the required tax.
In this article, we will guide you through everything you need to know about road tax in Haryana—how it is calculated, the current rates, and the convenient payment methods available to you. Read on to make sure you’re well-informed and up-to-date with the latest road tax guidelines in Haryana.
What is Road Tax and Why is it Important?
According to the state government regulations, road tax is an obligatory fee imposed on all vehicle owners who use their vehicles on the public roads. The tax is usually charged when registering the car, and it is crucial for the maintenance and security of roads. It ensures that the infrastructure required for efficient and easy transportation is well-financed.
The tax paid on roads across India varies depending on the types of vehicles, engine capacity, model, and vehicle cost. This tax is paid easily as vehicle owners can do so via online portals that the state transport department facilitates, and the process of payment is convenient and hassle-free.
Importance of Road Tax
Road tax is essential for several reasons:
- Generating Revenue: The tax finances the construction and maintenance of road infrastructure such as roads, highways and bridges to allow safe travel.
- Legal Requirement: It is a legal provision required by the Motor Vehicles Act of 1988. Failure to pay may lead to punishment, denial of a fitness certificate or even a seizure of vehicles.
- Vehicle Movement Regulation: Road tax also serves in checking traffic, ownership of vehicles, as well as promoting environmentally friendly sources of transport, and minimising pollution.
Road Tax Rules in Haryana
Road tax is imposed in Haryana according to the nature, price, and use of the vehicle, as stated in the Haryana Motor Vehicle Taxation Act, 2016. In the case of a private vehicle, it is usually a single tax as per the ex-showroom price of the vehicle.
Taxis with two wheels pay tax amounts ranging between 2-8% based on cost, whereas four-wheelers pay 5% (up to ₹6 lakh), 8% (₹6-20 lakh) and 10% (above ₹20 lakh). Commercial vehicles usually pay quarterly or annual taxes at a higher rate.
Applicability of Road Tax in Haryana
Any vehicle registered with the Haryana Transport Department must pay road tax. The tax applies to:
- Private Vehicles: Motorcycles, scooters, and cars that are for personal use.
- Commercial Vehicles: Trucks, taxis, buses, and goods carriers that pay recurring tax.
- Out-of-State Vehicles: Vehicles brought from other states must pay road tax for re-registration or temporary use.
Factors Affecting Road Tax Rates
The following factors influence Haryana road tax:
- Vehicle Type & Usage: Private cars have a lower tax rate than commercial vehicles, which are used for moving goods or passengers, and typically incur higher tax rates.
- Ex-showroom Price: Higher-priced vehicles fall into higher tax slabs.
- Engine Capacity/Vehicle Weight: Larger engines or heavier vehicles incur additional tax.
- Vehicle Age: Older vehicles may be eligible for rebates on re-registration.
- Fuel Type: Diesel vehicles may be taxed more; EVs may receive concessions.
Lifetime Tax, Green Tax, and Exemptions
- Lifetime Tax: One-time tax for non-transport vehicles.
- Green Tax: Levied on older vehicles to control pollution.
- Exemptions: Agricultural vehicles, ambulances, and vehicles for disabled persons may get exemptions.
How to Calculate Road Tax in Haryana?
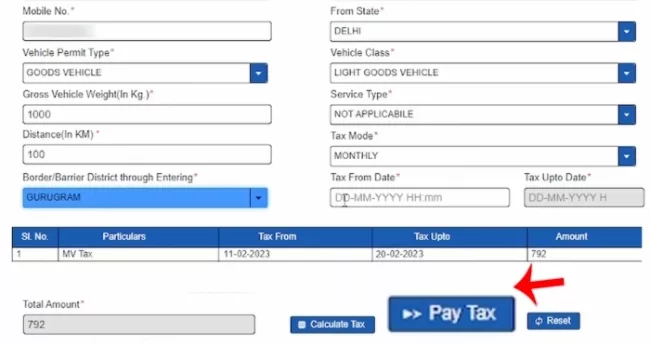
Haryana road tax is levied under the Haryana Motor Vehicle Taxation Act, 2016 and is determined by the type, cost, and usage of the vehicle.
Commercial vehicles are taxed differently, based on seating capacity, weight, or usage, and payments are usually made quarterly or annually. Other factors such as the vehicle’s age, engine capacity, and fuel type (diesel, petrol, or electric) also affect the tax amount.
Parameters Used for Road Tax Calculation
The table below discusses the standard parameters used for road tax calculation:
| Factors | Description |
| Type of the Vehicle | Two-wheelers, cars, SUVs, buses, trucks, and commercial vehicles |
| Capacity of the Engine | Measured in CC (cubic centimetres); higher CC means higher tax |
| Weight of the Vehicle | Heavier vehicles, such as SUVs, attract more tax than lighter models |
| Usage | Personal vehicles pay lower tax compared to commercial vehicles like taxis, trucks, and buses |
| Fuel Type | Petrol, diesel, CNG, and electric vehicles (EVs often enjoy concessions) |
| Age of the Vehicle | New vehicles attract higher tax, while older vehicles may get rebates |
| Price or Value of the Vehicle | Road tax is usually a fixed percentage of the vehicle’s ex-showroom cost |
Sample Road Tax Calculation for Different Vehicles
The table below shows how road tax rates vary depending on the type and price of vehicles in Haryana:
| Vehicle Type | Price | Tax Rate | Road Tax Payable |
| Hatchback | Below ₹5,00,000 | 5% | ₹25,000 |
| Electric Car | ₹12,00,000 | 4% | ₹48,000 |
| SUV | ₹20,00,000 | 10% | ₹2,00,000 |
| Luxury Car | ₹40,00,000 | 10% | ₹4,00,000 |
Disclaimer: Actual road tax in Haryana may vary based on the latest RTO updates, vehicle location, and specific vehicle configurations.
How to Pay Road Tax in Haryana?
Haryana road tax is determined by multiple factors, such as the vehicle’s engine capacity, category, purpose of use, and its ex-showroom price.
Different tax slabs apply to two-wheelers and four-wheelers depending on their cost, while commercial and luxury vehicles are charged at higher rates. In most cases, road tax in Haryana is collected as a one-time payment at the time of vehicle registration.
Online Payment Process
Payment of road tax in Haryana can be done easily through the state’s official online system. This makes the process quicker, transparent, and time-saving. Follow the steps below to pay your road tax online:
- Step 1: Visit the official Parivahan website, Parivahan Portal.
- Step 2: Select the “Vahan Service.”
- Step 3: Enter your vehicle registration number, select Haryana as the state, and choose the respective RTO.
- Step 4: Click on “Online Services” and then select “Pay Vehicle Tax.”
- Step 5: Enter the last five digits of your Chassis Number and click on “Validate Regn_no/Chasi_no.”
- Step 6: Generate an OTP, which will be sent to your registered mobile number. Enter the OTP and proceed.
- Step 7: Update your valid Insurance details and review the fee panel displayed.
- Step 8: Pay the road tax online using net banking, debit/credit card, or UPI.
- Step 9: Download the receipt generated after successful payment. The application will be forwarded to the RTO for further verification.
Offline Payment Process
If you prefer to pay road tax offline in Haryana, you can do so at the nearest Regional Transport Office (RTO) or an authorised collection centre. The steps are as follows:
- Step 1: Visit the nearest Haryana RTO or an authorised tax collection centre.
- Step 2: Carry all required documents, such as RC, ID proof, and insurance copy.
- Step 3: Collect and fill out the road tax payment form available at the RTO.
- Step 4: Submit the form along with the necessary documents
- Step 5: Pay the applicable tax amount through cash, cheque, or demand draft.
- Step 6: Collect the payment receipt from the RTO, which serves as formal proof of road tax payment.
Documents Required for Road Tax Payment
When paying road tax in Haryana (online or offline), the following documents are required:
- Vehicle invoice copy
- Vehicle Registration Certificate (RC)
- Valid Vehicle Insurance copy
- No Objection Certificate (NOC) (for vehicles from another state)
- Form KMVT14 (for out-of-state vehicles)
- Proof of Address (Aadhaar Card, Passport, Voter ID, Ration Card, Rental Agreement, or Utility Bill)
Penalties for Late Payment of Road Tax in Haryana
As per the Haryana Motor Vehicle Taxation Act, 2016, delays in payment of road tax will cause penalties, as follows:
| Delay Situation/Period | Penalty/Fine |
| Delay in payment (general) | 50% – 100% of the arrears in road tax |
| First-time offence | Fine equals 2 quarters of road tax |
| Repeat offences | Fine equal to or more than annual tax (up to 2x yearly tax) |
| Minimum fine | ₹300 (cannot be less than this amount) |
| Previous conviction under Section 16 of the Act | ₹500 – up to double the tax payable on the vehicle |
Note: The actual penalty may vary depending on the RTO’s evaluation and case-specific circumstances.
Refunds and Road Tax Transfer Rules in Haryana
Vehicle owners may obtain a refund of road tax provided the following criteria are met:
Conditions for Road Tax Refund
Vehicle owners in Haryana may claim a refund of road tax under the following situations:
- Selling the Vehicle: If the vehicle is sold before the tax validity period expires.
- Inter-state Transfer: When transferring the vehicle to another state (since fresh road tax is to be paid there).
- Vehicle Disposal: If the vehicle is scrapped before the RC’s validity period (15 years).
Procedure for Applying for a Road Tax Refund/Transfer
Follow the steps below to apply for a refund or transfer of road tax in Haryana:
- Step 1: Visit the RTO where your vehicle is registered.
- Step 2: Fill out the refund/transfer application form.
- Step 3: Submit the necessary documents, including RC, original tax receipt, proof of scrapping/relocation, and NOC (if moving to another state).
- Step 4: The RTO will verify your request and process the refund or transfer based on the remaining tax period and the vehicle’s age.
Comparison: Road Tax in Haryana vs Other States
The following table provides a comparison of road tax for a ₹10 lakh private car and the electric vehicle (EV) tax status in nearby states:
| State | Road Tax for Car (₹10L) | Electric Vehicle Tax |
| Haryana | ₹50,000 (5%) – ₹80,000 (8%) | 100% Exempt |
| Punjab | ₹95,000 – ₹1,30,000 (9.5% – 13%) | 100% Exempt |
| Delhi | ₹1,00,000 – ₹1,50,000 (10% – 15%) | 100% Exempt |
| Maharashtra | ₹1,10,000 – ₹1,30,000 (11% – 13%) | 100% Exempt |
| Kerala | ₹1,30,000 – ₹1,60,000 (13% – 16%) | 5% up to ₹15 lakh |
Note: Haryana offers lower road tax rates compared to neighbouring Punjab and Delhi, making it more cost-friendly for vehicle owners. Additionally, like other states, Haryana has exempted electric vehicles (EVs) from road tax to encourage eco-friendly transport.
Road tax in Haryana plays a vital role in maintaining road infrastructure and ensuring efficient transport across the state. The tax rates vary depending on the type of vehicle, its cost, usage, and fuel category.
Vehicle owners can easily calculate and pay their dues online through the Haryana Transport Department portal, making the process simple and accessible. Staying updated with the rules helps avoid penalties and ensures hassle-free vehicle ownership and smooth travel across the roads of Haryana.
FAQs about Road Tax in Haryana
Can I get a refund of road tax in Haryana?
Yes, vehicle owners are eligible for a refund of road tax in specific cases. The refund is processed by the Regional Transport Office (RTO) where the vehicle is registered.
Under what conditions is a road tax refund applicable in Haryana?
You may claim a refund if:
The vehicle is sold before the validity of the paid tax expires.
The vehicle is transferred to another state, where fresh tax is payable.
The vehicle is scrapped or disposed of before completing the RC validity period (15 years).How often is road tax paid in Haryana?
For private vehicles, road tax is generally a one-time payment made at the time of registration. In contrast, for commercial vehicles, road tax is usually paid quarterly or annually, depending on the vehicle type and usage.
What happens if I delay the payment of road tax in Haryana?
Delayed payment attracts penalties under the Haryana Motor Vehicle Taxation Act, 2016:
A penalty of 50%–100% of the arrears in road tax.
For a first-time offence, a fine equal to two quarters of tax.
For repeat offences, a fine equal to or higher than the annual tax (up to 2x).
A minimum fine of ₹300 applies.
If convicted under Section 16, fines may range from ₹500 up to double the tax payable.Are there exemptions or reduced road tax rates in Haryana?
Yes, certain categories enjoy exemptions or reduced rates:
Electric vehicles (EVs): Reduced or waived road tax under recent green initiatives.
Agricultural vehicles (tractors, harvesters, etc.): Concessional rates or exemptions.
Government and defence vehicles: Usually exempt.





